RF Calibration
- Updated2023-02-21
- 3 minute(s) read
Each user calibration type has a variety of implementations. Which method you use depends on the DUT, test system, and measurement requirements. The following four methods are commonly used in network analyzer calibration.
- Automatic Calibration (AutoCal)
- Short-Open-Load-Through (SOLT) Calibration
- Short-Open-Load-Reciprocal (SOLR) Calibration
- Through-Reflect-Line (TRL) Calibration
Standard Calibrations
With user calibration, various standards are used to calibrate the number of discrete frequency points configured for the sweep. Refer to the NI-VNA LabVIEW and C/CVI Reference sections for information about how to configure the frequency range and number of frequencies for the sweep.
Changing some NI-VNA settings after running a calibration invalidates the calibration. These settings include the following NI-VNA properties and attributes, which are described in more detail in the NI-VNA Programming section of this help file.
- IF bandwidth
- Source power
- Averaging type
- Frequency sweep characteristics
- Measurement enabled properties/attributes
- Calibration type
- Port connector gender and type
- Most AutoCal module properties/attributes
The one-port calibration is a short/open/load (SOL) calibration that removes source match, directivity, and frequency response errors. The one-path two-port calibration is a short/open/load/through (SOLT) calibration. Full, two-port calibrations can be completed with a through-reflect-line (TRL) calibration or a short/open/load/through (SOLT) calibration. Both TRL and SOLT calibration remove transmission response errors and transmission source match errors in addition to reflection error terms. You can also perform a reflection response calibration or a transmission response calibration, which corrects the frequency response of the respective path. Reflection response calibration requires an open connected to PORT 1, and transmission response calibration requires a through standard connected between PORT 1 and PORT 2.
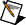 |
Note Reduced measurement accuracy may occur if you use a one-path two-port calibration instead of a full two-port calibration, because the one-path two-port calibration does not account for the load match of port two. |
The following figure provides a state diagram for the NI-VNA calibration process.

For information about how to complete a calibration of your NI-VNA device using the NI-VNA SFP, refer to Performing an Automatic Calibration (AutoCal) Using the NI-VNA SFP, Performing a Manual Calibration Using the NI-VNA SFP, or Performing a User Calibration Using the NI-VNA API.
Calibration and Correction
When the device has a valid calibration, you can choose whether to "correct" the measurements by understanding the relationship between enabling correction and the calibration. This relationship is shown in the following table.
| Correction Enabled | Calibration State | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Uncalibrated | Calibrated | Calibrating | |
| FALSE | NI-VNA does not have a valid set of calibration data for the current device configuration. Measurement data is not corrected using calibration data. | NI-VNA does have a valid set of calibration data for the current device configuration; however, measurement data is not corrected using calibration data. | N/A |
| TRUE | NI-VNA does not have a valid set of calibration data for the current device configuration; however, measurement data is modified using (potentially invalid) calibration data. | NI-VNA does have a valid set of calibration data for the current device configuration. Measurement data is corrected using calibration data. | N/A |