Transitioning from Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) to NI-DAQmx Using ANSI C and NI LabWindows™/CVI
Overview
This four-part series helps you transition from Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) to NI-DAQmx in the ANSI C and NI LabWindows™/CVI programming languages.
NI is phasing out the Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) driver. The recommended new driver, NI-DAQmx, is designed for use with some of the newest data acquisition devices available from NI.
Refer to the “Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) Overview” and “NI-DAQmx Overview” sections for more information about the different available solutions.
Contents
- Accessing Help in NI-DAQmx
- Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) Overview
- NI-DAQmx Overview
- Installation Instructions for the ANSI C NI-DAQmx API
- Identifying Your Measurement
- Additional Resources
Accessing Help in NI-DAQmx
This series references two manuals that are shipped with NI-DAQmx.
- NI-DAQmx Core Help – references the language-agnostic manual for NI-DAQmx. The NI-DAQmx Core Help explains NI-DAQmx concepts and provides background about the various features and capabilities of the driver. Refer to Start»Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help to access this manual.
- NI-DAQmx C Reference Help – references the manual for the DAQmx C API. This reference is specific to the C API and provides documentation for NI-DAQmx function calls. There are also concept topics specific to using the DAQmx C API. Part of the NI-DAQmx driver software, this manual is located at Start»All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx C Reference Help.
Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) Overview
Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) is a library of routines that work with NI data acquisition (DAQ) devices. Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) helps you perform tasks ranging from simple device initialization to advanced high-speed data logging. The types of data acquisition devices and the complexity of your applications determine the number of tasks you need.
Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) is an older driver with outdated application programming interfaces (APIs) for developing data acquisition, instrumentation, and control applications for older NI DAQ devices. You should use Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) only in the following circumstances:
- You have a device that is not supported by NI-DAQmx, such as an E Series multifunction DAQ device.
- You are using a version of NI LabVIEW, LabWindowsTM/CVITM, or Measurement Studio lower than Version 7.0.
- You are upgrading from NI-DAQ 6.9.x and have existing applications that you do not want to port to NI-DAQmx at this time.
Refer to the NI-DAQ Readme file for more information about when to use Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy), including a complete list of supported devices, operating systems, application software versions, and language versions.
In the following section, learn about the NI-DAQmx driver and the DAQmx ANSI C API as well as explore some of the advantages these provide over Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy).
See Also:
NI-DAQmx Overview
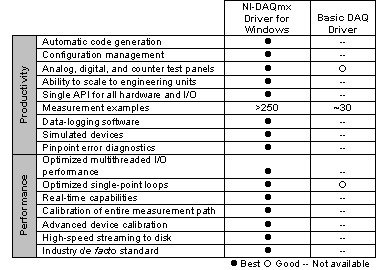
NI-DAQmx is the new NI data acquisition driver framework that addresses several weaknesses present in Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy).
Some of the advantages of NI-DAQmx include:
Performance
- NI-DAQmx provides significant performance improvements over Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy), especially for single-point software-timed analog input.
Measurement-Based API
- The API for NI-DAQmx relates to the type of measurement you make. With the API abstraction, you can specify hardware behavior based on the hardware subsystem.
Multithreaded Driver
- Using the NI-DAQmx driver, you can easily set up concurrent I/O operations and create multithreaded data acquisition systems.
Improved State Model
- NI-DAQmx defines and enforces a state model, eliminating unnecessary reconfigurations of input limits, timing, triggering, and accessories. This improvement significantly increases overall performance.
Consistent API across all Programming Languages
- The NI-DAQmx programming paradigm is consistent across multiple languages. You do not have to reacquaint yourself with NI-DAQmx driver concepts if you decide to move between programming NI-DAQmx in LabVIEW, ANSI C, C++, C #, and Visual Basic .NET.
Robustness in Exceptional Conditions
- Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) can have difficulty handling exceptional conditions, such as abnormal process termination. NI-DAQmx defines and enforces policies for such conditions.
Note: For additional information see Answers to Frequently Asked Questions about NI-DAQmx and Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy).
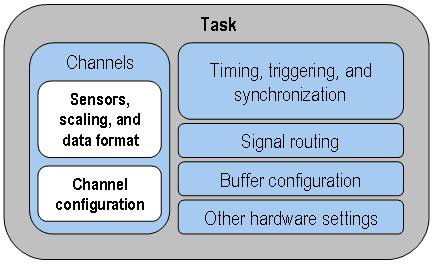
The NI-DAQmx data acquisition framework introduces several new concepts, the two most important being tasks and task state models.
Learn how tasks are set up as you explore the NI-DAQmx ANSI C API in the following sections.
Task State Model
NI-DAQmx uses a task state model to improve ease of use and speed up driver performance. The task state model consists of five states – Unverified, Verified, Reserved, Committed, and Running.
You can choose to interact with as little or as much of the task state model as your application requires.
For more information about the NI-DAQmx task model, select NI-DAQmx Help»Key NI-DAQmx Concepts»Tasks»Task State Model in the NI-DAQmx Core Help.
The NI-DAQmx Core Help provides information about some of the other concepts of NI-DAQmx as well. For more information, select NI-DAQmx Help»Key NI-DAQmx Concepts.
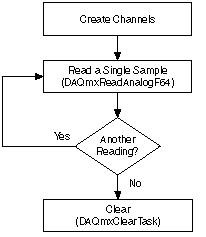
Flowcharts
The NI-DAQmx Core Help has flowcharts for each type of task. You can find these flowcharts under NI-DAQmx Help»Common Applications»Generic Programming Flows .
Typical NI-DAQ Application
When framing a data acquisition application, regardless of the type of driver or device used for acquiring data, you organize the application into five main steps. The approaches to these five steps vary based on how the data acquisition driver is organized and the functionality it provides. These steps include the following:
1. Identify your measurement
2. Configure your measurement
3. Run the data acquisition operation
4. I/O
5. Clean up
These steps are the basic building blocks for creating a typical data acquisition application. You should be familiar with how a data acquisition application uses the NI-DAQ driver to address each of these steps and create an effective data acquisition application. Other documents in this series compare the NI-DAQmx ANSI C API with the Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) ANSI C API by breaking down their functionality into these five steps. Refer to the “Additional Resources” section to access these documents.
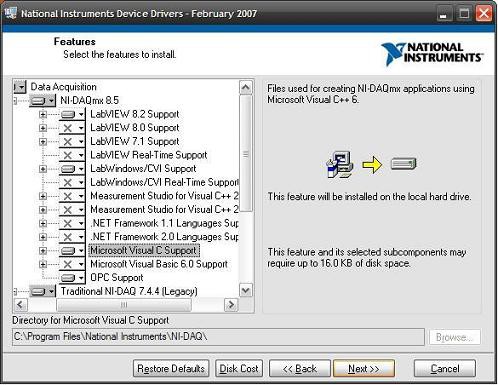
Installation Instructions for the ANSI C NI-DAQmx API
The DAQmx ANSI C API is available as part of the NI-DAQmx driver. Installing support for Microsoft Visual C Support installs the NI-DAQmx shipping examples and the API reference and concept documents. The ANSI C API is available for free as part of NI-DAQmx. LabWindowsTM/CVITM Support installs the examples and function panels.
ANSI C Shipping Examples for NI-DAQmx
ANSI C shipping examples for the NI-DAQmx C API are installed as part of the language support and are available under Start»All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»Text-Based Code Support»ANSI C Examples.
LabWindowsTM/CVITM examples can be found in the NI Example Finder under Hardware Input and Output»DAQmx .
NI-DAQmx Quick Start Guide
The NI-DAQmx Quick Start Guide is a great document to get your data acquisition system up and running. It introduces setting up and installing NI DAQ devices on your machine and provides information about the various programming interfaces available for NI-DAQmx. For information about the programming interfaces and how to get started, refer to the “Getting Started Developing an Application” section in the NI-DAQmx Quick Start Guide. You can find the Quick Start Guide at Start»Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»DAQ Quick Start Guide.
Identifying Your Measurement
Before writing any code, you need to identify what kind of measurement you require.
Are you measuring temperature, strain, position, or another type of measurement? Are you using external sensors that need calibration or excitation? Will the sensor data require scaling of any kind? See DAQ Multifunction I/O Cable and Accessory Compatibility to select the correct cables and terminal blocks.
Once you have a good understanding of the type of measurement you are making, the next step is to configure the operation. Refer to “Transition from Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) to NI-DAQmx using ANSI C or LabWindowsTM/CVITM: Part II” for information on configuring your operation.
Additional Resources
- Transitioning from Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) to NI-DAQmx Using ANSI C and LabWindows/CVI: Part Two
- Transitioning from Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) to NI-DAQmx Using ANSI C and LabWindows/CVI: Part Three
- Transitioning from Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy) to NI-DAQmx Using ANSI C and LabWindows/CVI: Part Four
- What is LabWindows/CVI?
- Answers to Frequently Asked Questions about NI-DAQmx and Traditional NI-DAQ (Legacy)
The mark LabWindows is used under a license from Microsoft Corporation.