SCB-100 and SCB-100A : DAQ Multifunction I/O Accessory Guide
Overview
This guide addresses many common questions for the SCB-100 and SCB-100A 100-pin DAQ breakout connector or terminal blocks, which allow you to easily interface analog, digital and counter input and output signals. Whether you need mounting information, mappings or pinouts for wiring, to understand the DIP switches or feedthrough modes, or to create custom configuration, this guide provides a short summary, and then link to other resources, such as manuals, specifications, dimensional drawings, and more.
Contents
- Using this DAQ Accessory Guide
- Differences and Similarities between with SCB-100 and SCB-100A
- Quick Specifications, Manuals, Quick Reference Labels, and Dimensional Drawings
- Wiring Your SCB-100 or SCB-100A Terminal Block
- Understanding Feedthrough Modes and the SCB-100 DIP Switches
- Mounting your SCB-100A
- Compatible Devices, Modules, and Cabling for the SCB-100 and SCB-100A
- Additional Resources
Using this DAQ Accessory Guide
This guide is intended to cover the SCB-100 and SCB-100A 100-pin terminal blocks, which are designed for use with 100-pin NI DAQ Counter/Timer (TIO), Digital I/O (DIO), and Multifunction I/O (MIO) devices and modules.
- To find more information about other NI DAQ accessories and general information that applies to all DAQ accessories, visit DAQ Multifunction I/O Accessory Guide Main Page.
- To determine compatibility of your SCB-100 and SCB-100A with your NI DAQ device or module, or your NI DAQ cable, visit DAQ Multifunction I/O Cable and Accessory Compatibility.
- To create your own cable or test fixture, or to repair an NI DAQ cable or accessory, visit NI DAQ Device Custom Cables, Replacement Connectors, and Screws. First, note the connector information found on this page.
Differences and Similarities between with SCB-100 and SCB-100A
The SCB-100A, introduced in 2017, succeeded the SCB-100. The SCB-100A is recommended for all new designs for Digital I/O (DIO) and Counter/Timer (TIO) models. Both are 100-pin terminal block breakout accessories allowing wiring connectivity through screw terminals.
| SCB-100A | SCB-100 |
|---|---|
| Provides a direct breakout of the terminals on the device or module, using screw terminal connections. | |
| Upgraded design: magnetic lid, updated styling, and updated blue/silver color scheme. | Original design: hinged lid and off-white color scheme. |
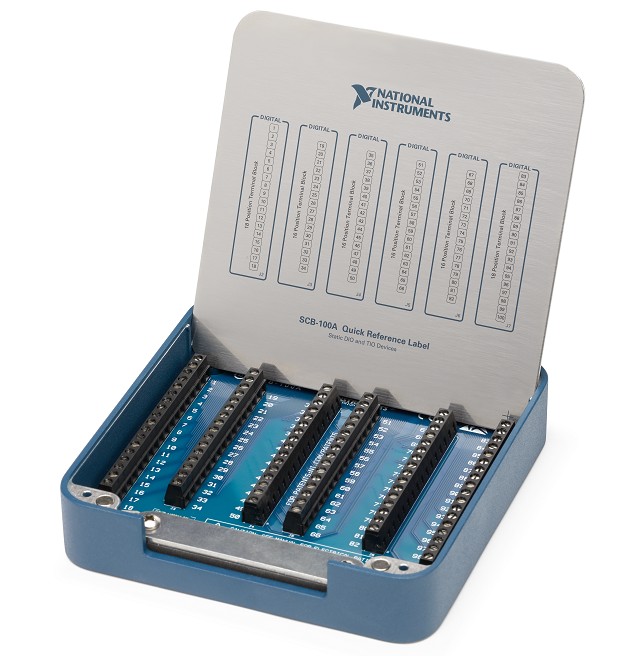 |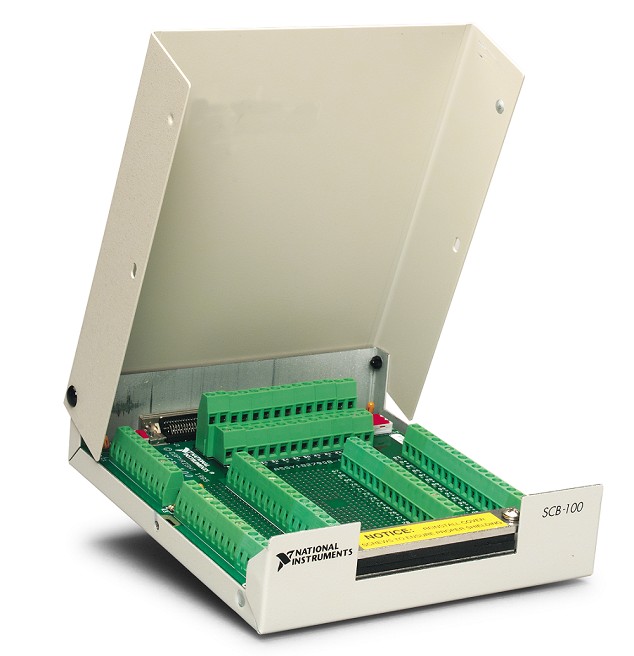  |
| No MIO functionality: No breadboard area and no DIP switches. | MIO functionailty: Features breadboarding area, and DIP switches. |
| Direct feedthrough mode only | Direct and enhanced feedthrough modes |
| No thermocouple support. | Features cold junction compensation (CJC) for accurate thermocouple temperature measurements. |
| Panel and wall mounting and DIN rail mounting options. | No panel, wall, or DIN rail mounting options. |
| Compatible with the same cables, devices, and modules, but SCB-100A only offers direct feedthrough mode. | |
Quick Specifications, Manuals, Quick Reference Labels, and Dimensional Drawings
This section contains a summary of information frequently sought when installing, wiring, or configuring the SCB-100 or SCB-100A. More detailed information can be found in the linked additional resources. Dimensional drawings can be downloaded for free and are available in 2D and 3D formats; they contain size measurements and other helpful information, and are available in several popular formats, such as PDF, AutoCAD (.dxf, and .igs (IGES)), STEP (.stp), and .prt (Pro/E). Model-specific reference labels are provided for many popular DAQ families; they can be printed and attached to your terminal block for quick wiring reference.
| SCB-100A Quick Specifications and Published Resources |
|---|
| Connector and Pinout Information |
100-pin 0.050 SCSI D-Type Connector Female (Receptacle)
|
| Physical Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Width | 14.7 cm (5.8 in.) |
| Depth | 14.7 cm (5.8 in.) |
| Height | 3.0 cm (1.2 in.) |
| Weight | 670 g (1 lb 7.6 oz) |
| For more information, refer to the User Guide and Specifications or Dimensional Drawing | |
| Screw Terminal Wiring Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Minimum wire gauge | 30 AWG |
| Maximum wire gauge | 16 AWG |
| Screw terminal torque | 0.5 to 0.6 N-m (4 to 5 in.⋅lb) |
| Spacing between screw terminals | 5.00 mm (0.19685 in.) |
| For more information, refer to the User Guide and Specifications. | |
| SCB-100 Quick Specifications and Published Resources |
|---|
| Connector and Pinout Information |
100-pin 0.050 SCSI D-Type Connector Female (Receptacle)
|
| Physical Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Width | 17.93 cm (7.06 in.) |
| Depth | 15.37 cm (6.05 in.) |
| Height | 4.50 cm (1.77 in.) |
| Weight | 897 g (1 lb 15.6 oz) |
| For more information, refer to the Installation Guide or Dimensional Drawing | |
| Screw Terminal Wiring Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Minimum wire gauge | 26 AWG |
| Maximum wire gauge | 14 AWG |
| Screw terminal torque | 0.5 to 0.6 N-m (4 to 5 in.⋅lb) |
| Spacing between screw terminals | 5.08 mm (.200 in.) |
| For more information, refer to the Installation Guide. | |
Wiring Your SCB-100 or SCB-100A Terminal Block
To easily wire sensors and signals to your terminal block, leverage the published documentation and information in this guide. Here are the basic steps to designing your measurement circuit diagram, understanding pin mapping, connecting your wiring, and configuring your terminal block. Failure to set up your terminal block properly may lead to no readings, unexpected readings, noisy readings, or possible damage to your terminal block, device, or module.
- The general concepts of pin mapping and pinouts are covered in the DAQ Accessory Guide Main Page. Notice that a common point of confusion for normal wiring is the need to first understand the cable mapping, or pinout at the connector found on your terminal block, which is not the case.
- The Installation Guides, User Guides, and Quick Reference Labels for the SCB-100 and SCB-100A are provided in the Quick Specifications and Published Resources section. These contain pinout or pin mappings, and also extended information for configuring your terminal block in the various modes that it supports, extending its functionality, and noise reduction, as described below.
- Once you've completed your wiring, make sure to finish by tightening the strain relief bar to ensure that your wires can not easily pull out from your terminal block.
- A common issue with analog signals is noisy or floating signals, even when using a shielded connector block, such as the SCB-100. These can be avoided by first understanding your measurement type, and creating a circuit diagram that allows you to wire and then ground your signals correctly.
- Review Field Wiring and Noise Considerations for Analog Signals. This guide contains extended information on noise reduction, and how to correctly wire differential (DIFF), Ground Referenced Single-Ended (RSE), and Nonreferenced Single-Ended (NRSE) measurement modes for floating signal sources and grounded signal sources.
- Common issues with thermocouple temperature readings, on the SCB-100 only, are typically due to incorrect DIP switch settings, understanding the cold junction compensation (CJC), understanding open thermocouple detection, and thermocouple input filtering.
- It is also important to consider using shielded signal wires, shielded cables, and ensuring that the terminal block itself has been correctly grounded.
- The breadboard, on the SCB-100, can be used to add custom circuitry. You may also need to install bias resistors, lowpass filtering, highpass filtering, resistors for current input measurement, voltage attenuation or division, and more. The installation guide referenced in this guide contains detailed information on when to do these setups, how to configure them, and other details such as soldering and desoldering information.
Understanding Feedthrough Modes and the SCB-100 DIP Switches
The SCB-100A does not feature DIP switches and only works in direct feedthrough mode. It does not need any additional settings to function as direct feedthrough.
Incorrectly setting the DIP switches and misunderstanding the feedthrough modes on your SCB-100 can result in a blown C4 capacitor, noisy readings, unexpected readings, or no readings at all. Further, if measuring thermocouples, understanding the onboard temperature sensor for cold junction compensation (CJC), and how to enable the various sensor modes is important to getting an accurate reading. Review your Installation Guide, or Compatible Devices, Modules, and Cabling for more information about compatibility of your NI device or module with the various modes.
Common issues with the DIP switches typically arise if you previously used your terminal block with another device or module, or are switching to or from taking thermocouple measurements.
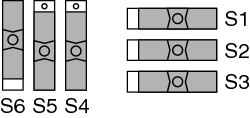
Direct Feedthrough Mode
In this mode:
- All 100 signals from the device break out directly to the screw terminals.
- The onboard temperature sensor is not used (SCB-100 only).
- +5 V power is not provided to the signal conditioning area of the accessory. (SCB-100 only)
Most supported devices and modules can only use this mode. This is the only mode available on the SCB-100A.
| SCB-100 |
|---|
 |
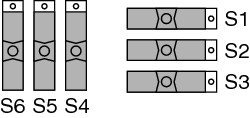
MIO with Disabled CJC Temperature Sensor Mode (Factory Default, SCB-100 Only)
In this mode:
- The onboard temperature sensor is not used.
- All device/module analog input (AI) lines (including AI 0 and AI 8) are accessible at the screw terminals.
- +5 V power is provided to the signal conditioning area of the accessory.
| SCB-100 |
|---|
 |
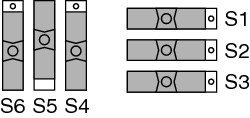
MIO with Single-Ended Temperature Sensor Mode (SCB-100 Only)
In this mode:
- The temperature sensor can be read using AI 0 in referenced single-ended (RSE) mode.
- All device/module analog input (AI) lines (except AI 0) are accessible at the screw terminals.
- +5 V power is provided to the signal conditioning area of the accessory.
| SCB-100 |
|---|
 |
MIO with Differential Temperature Sensor Mode (SCB-100 Only)
In this mode:
- The temperature sensor can be read using AI 0 and AI 8 in differential mode.
- All device/module analog input (AI) lines (except AI 0 and AI 8) are accessible at the screw terminals.
- +5 V power is provided to the signal conditioning area of the accessory.
| SCB-100 |
|---|
 |
Mounting your SCB-100A
- DIN Rail Mounting - The NI 9913 DIN rail mounting kit (part number 781740-01) contains one clip for mounting the SCB-100A on a standard 35 mm DIN rail. Refer to the NI SCB-100A User Guide for more information.
- Panel or Wall Mounting - To panel or wall mount the SCB-100A, refer to the instructions in the NI SCB-100A User Guide. Without scaling or resizing, print the referenced Panel Mounting Template that corresponds with your paper format. Use the printout as your mounting template. Extended information can be found on the 2D drawings and the 3D models for the SCB-100A, and are available through the referenced Dimensional Drawings.
Note: The SCB-100 does not offer mounting options.
Compatible Devices, Modules, and Cabling for the SCB-100 and SCB-100A
Some devices and modules listed in the table have extended compatibility information, which is linked to in their Compatibility Guide. Refer to your device or module's user manual or user guide for more information.
Supported Features:
- All - (SCB-100 Only) All of the extended functionality that the SCB-100 has to offer is supported, including: direct feedthrough mode, thermocouple measurements, open thermocouple detection, current input, filtering, and voltage dividers.
- Direct only - Direct feedthrough mode is the only supported mode. If you are using the SCB-100, the DIP switches must be set to direct feedthrough mode.
| Device or Module | Supported Features | Shielded Cable | Unshielded Cable |
|---|---|---|---|
| NI DAQ Models | |||
| NI 60xxE (formerly E Series) 100-pin Models | All | See Compatibility Guide | |
| NI 65xx (formerly Digital I/O [DIO] Series) 100-pin Models | Direct Only | See Compatibility Guide | |
| NI 66xx (formerly Timing I/O [TIO] Series) 100-pin Models | Direct Only | See Compatibility Guide | |
Additional Resources
Documentation
- Learn about specifications, model differences and other common questions for other DAQ accessories.
- Learn about the compatibility of NI DAQ devices and modules with NI DAQ cables and accessories.
- Find the parts needed to make a custom cable, breakout fixture, or replace connectors and screws on NI DAQ hardware.
- Browse and search NI manuals, guides, specifications, datasheets, getting started and more.
- Browse dimensional drawings for NI DAQ cables and accessories.
- Purchase NI cables
- Purchase NI terminal blocks and connector blocks