Comparison of FOUNDATION Fieldbus and Traditional Systems
Contents
Background
FOUNDATION Fieldbus (FF) is a Local Area Network (LAN) for process control sensors, actuators, and control devices. It is a digital, two-way, multi-drop network positioned to replace proprietary networks that connect Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) of many big companies. In traditional systems, a computer or expensive controller unit provides control for the network of devices. In recent years, some companies have developed instrument systems with more intelligence built into the devices. The main drawback of these systems is that they are proprietary and thus not interoperable. There are other open instrumentation standards, such as PROFIBUS and HART, but these protocols do not implement control -- a separate controller is still required. FF is an open standard that allows the field devices to run both the input/output and the control.
Traditional systems in this market are known as 4-20 mA systems, so named for the signal levels that control the devices. These devices take input measurements and send the information to a control unit for processing. The computer then performs the necessary calculations and tells devices what their outputs should be. To get a device's serial number or to calibrate or test a device in the field, a person would have to walk (or drive) to the physical device. With FF, these types of things can be done directly from the control room. What if the computer that is running the control goes down? In a traditional system, the devices would go into some pre-defined fail-safe mode, leaving the pumps, valves, and other equipment without any interactive control until communication with the computer resumes. With FF, control is brought down to the device level. After downloading the configuration, your control loop (a PID loop, for example) continues operating even if the monitoring computer is disconnected.
4-20 mA System
| Smart Instruments
| FOUNDATION Fieldbus
| |
| Interoperability & Interchangeability | OPEN, interoperable, interchangeable. | PROPRIETARY, limited interoperability, no interchangeability. | OPEN, interoperable, interchangeable. |
| Variety & Availability of Equipment | Wide variety. Multiple suppliers. | Limited. The customer can use only the offerings of one supplier. | Actual FF devices are limited but growing. There are, however, many ways of incorporating standard 4-20 mA devices into an FF network. |
| Communication | One variable. One direction. | Multiple variables. Two-way. | Multiple variables. Two-way. |
| Wiring | Point-to-point. | Point-to-point or multi-drop. | Multi-drop. |
Table 1: Comparison of FOUNDATION Fieldbus and traditional systems.
Similarities
- Uses existing twisted-pair wiring
- Uses existing terminal blocks
- Similar wiring practices
- Provides for Intrinsic Safety (IS) requirements (for hazardous areas)
- Provides for power supply redundancy
- Enables loop-powered instruments
Differences
- FF communication is digital; 4-20 mA communication is analog
- FF connects field devices in parallel; 4-20 mA connects field devices in series
- FF requires a terminator at each end (resistor and capacitor)
- FF requires an impedance-matched power supply
Benefits
- Distributed control, meaning that control is not done by the monitoring computer. It is brought down into the devices themselves.
- Open standard, meaning that a customer can choose products from different vendors. The Fieldbus Foundation is the organization that defines the FOUNDATION Fieldbus specification and certifies products to be compliant with the standard. This guarantees that products from different vendors can be used interchangeably. The Fieldbus Foundation standardized the way the user canbring new devices into the network, set them up, and configure them. The building block in this system is the Device Description (DD). The DD tells everything about the device and its functionality. The DD lets you put an FF-certified device onto the network, import the vendor-supplied DD file into your configuration, and be ready to run. Any company with the proper resources can make an FF device (if it passes the Interoperability Test) that will work with all other FF-certified devices and software.
- The ability to use existing 4-20 mA wiring.
- Drastically reduced wiring costs. You only need one twisted wire pair that will carry multiple signals AND power, and you can drop devices off the network at any point. Since FF requires only a single set of wires to connect multiple devices, this dramatically reduces wiring costs from 4-20 mA systems, which required one pair of wires per device. Note that most, but not all devices have the option of being bus powered.
- Reduced need for controllers and other hardware.
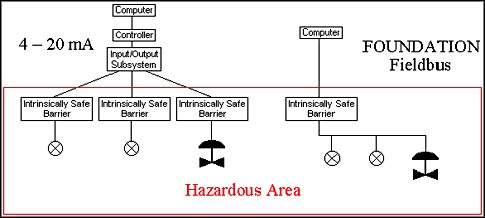
The following figure illustrates the reduced wiring and hardware requirements. Notice that the traditional implementation requires one IS barrier and a set of wires for each device for a total of 3 barriers and 3 sets of wires. The FOUNDATION Fieldbus implementation requires only one IS barrier and one set of wires for multiple devices.
Figure 1: Wiring comparison of FOUNDATION Fieldbus and traditional systems.