Converting a Camera Link Application from the NI-IMAQ API to the NI-IMAQdx API
Contents
- Supported Software & Hardware
- Reasons to switch to the NI-IMAQdx API
- Primary differences between the NI-IMAQ API and the NI-IMAQdx API
- Migrating from NI-IMAQ to NI-IMAQdx
Supported Software & Hardware
- Vision Acquisition Software 2018 and later
- PCIe-1427, PCIe-1433, PCIe-1437 and PXIe-1435
Reasons to switch to the NI-IMAQdx API
The NI-IMAQ API is not available in LabVIEW NXG. Using the NI-IMAQdx API for Camera Link applications allows users to convert their existing LabVIEW applications from the NI-IMAQ API to the NI-IMAQdx API and then migrate the converted application to LabVIEW NXG. Alternatively, a new Camera Link application can be developed directly in LabVIEW NXG.
The NI-IMAQdx API now serves as a unified API, allowing users to more easily switch between popular camera types, such as GigE Vision and USB3 Vision, and Camera Link without having to rewrite large portions of the acquisition engine for the given application.
Primary differences between the NI-IMAQ API and the NI-IMAQdx API
The following are several key differences between the NI-IMAQ API and the NI-IMAQdx API that should be considered when porting an existing application.
Region of Interest
The NI-IMAQ acquisition VIs offer the option of specifying a Region of Interest (ROI). The NI-IMAQdx VIs do not have this option and will return the full image every time. If you need a specific ROI, you must configure the NI-IMAQdx attributes “FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::OffsetX”, “FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::OffsetY”, “FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::Width”, and “FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::Height”.
Acquisition Timeout
In NI-IMAQ, the acquisition timeout (the amount of time to wait for an image before returning an error) is configured through the LabVIEW property node by setting the value for “Acquisition Parameters:Frame Timeout (ms)”. In NI-IMAQdx, the timeout is an input to each acquisition VI and defaults to 5000 ms (e.g. “IMAQdx Snap2.vi”, IMAQdx Grab2.vi”, “IMAQdx Sequence2.vi”, “IMAQdx Get Image2.vi”, and “IMAQdx Extract Image.vi”). You can configure the timeout through the NI-IMAQdx property node as well by setting the value for “AcquisitionAttributes::Timeout”. To use this value, you must pass in -2 to the timeout input for the NI-IMAQdx acquisition VIs.
Triggering and Digital I/O
In NI-IMAQ, trigger and I/O line configuration, including pulse generation, is performed through the VIs located in the “Signal I/O” palette. In NI-IMAQdx, this configuration is done by setting attributes through the property node. It is strongly recommended to look at the NI-IMAQdx Compatibility for NI-IMAQ API (see the “Compatibility VIs” section for the location of the VIs) and example VIs to see how to do this. Triggering and I/O can also be configured for NI-IMAQdx by using NI-MAX. Saving the configuration in NI-MAX will persist these triggering and I/O settings to the camera file, and these settings will be applied to any session opened for the given device.
Bayer Decoding
When using Bayer encoded images, the NI-IMAQ acquisition VIs will return a monochrome image that must be passed to “IMAQ Bayer to RGB” VI to do the decoding into an RGB image. In NI-IMAQdx, the Bayer decoding is performed before returning the images from the acquisition VIs when performing a Grab acquisition, so there is no need to call this extra decoding VI. However, when performing a Ring acquisition, decoding the image in software prior to returning the image is not supported. In this case, you can perform the Bayer decoding on the frame grabber (if using the PCIe-1437), perform the Bayer decoding on the camera and acquire an RGB image, or acquire a raw monochrome image and decode the image with the “IMAQ Bayer to RGB” VI as done when using the NI-IMAQ API.
Buffer Numbers
The buffer numbers in the NI-IMAQ API are 28 bits. Values larger than 28 bits are reserved by the NI-IMAQ driver. The buffer numbers in the NI-IMAQdx API are only 24 bits. This means that it may be necessary to rewrite any logic that deals with specific buffer numbers to handle the change in the rollover value of the reported buffer number.
When acquiring images using “IMAQdx Get Image2.vi” or “IMAQdx Extract Image.vi”, NI-IMAQdx allows the user to specify the Buffer Mode, which obviates the need to specify the buffer number input in many common cases. See the documentation for those VIs for more details.
C Interface
While the LabVIEW APIs for NI-IMAQ and NI-IMAQdx are similar, the C APIs are not. Like the LabVIEW API for NI-IMAQdx, the C API for NI-IMAQdx also uses the Vision image. However, the NI-IMAQ C API uses raw buffers. For this reason, the image/buffer management is very different between the two driver C APIs. Unlike in LabVIEW, there is no compatibility API that is provided to aid in migrating an NI-IMAQ C application to NI-IMAQdx. The recommendation is to use the NI-IMAQdx examples to demonstrate how to use the NI-IMAQdx API in a C application. See the “Attribute Translation” and “Additional NI-IMAQdx Attribute” sections for help with mapping NI-IMAQ attributes and functionality to NI-IMAQdx attributes.
Migrating from NI-IMAQ to NI-IMAQdx
There are two ways to port from the NI-IMAQ API to the NI-IMAQdx API:
- Use the NI-IMAQdx Compatibility for NI-IMAQ API (see the “Compatibility VIs” section for the location of the VIs) for a more seamless transition. For NI-IMAQ VIs that do not have a direct replacement in the NI-IMAQdx API, we provided a library of functions that have similar input/outputs to NI-IMAQ VIs but use the NI-IMAQdx driver in the background. This method will require you to mix and match NI-IMAQdx VIs that have a direct NI-IMAQ correspondence and the provided compatibility VIs.
- Use the NI-IMAQdx driver directly. This option allows for the most code reuse between Camera Link and other camera types supported by NI-IMAQdx.
Direct VI Mapping
For some NI-IMAQ VIs, there is a direct correspondence with the NI-IMAQdx VIs. The NI-IMAQ VIs in this list can be replaced with the corresponding NI-IMAQdx VI without any changes. If an NI-IMAQ VI in this list has an input terminal that is not found in the corresponding NI-IMAQdx VI (e.g. Step x, Step y, Channel, Region of Interest), this feature is not implemented in NI-IMAQdx.
NI-IMAQ VI Name | NI-IMAQdx VI Name |
IMAQ Init.vi | IMAQdx Open Camera.vi |
IMAQ Close.vi | IMAQdx Close Camera.vi |
IMAQ Grab Setup.vi | IMAQdx Configure Grab.vi |
IMAQ Start.vi | IMAQdx Start Acquisition.vi |
IMAQ Stop.vi | IMAQdx Stop Acquisition.vi |
IMAQ Serial Read.vi | IMAQdx Serial Read.vi |
IMAQ Serial Read Bytes.vi | IMAQdx Serial Read Bytes.vi |
Figure 1. One-to one mapping of NI-IMAQ to NI-IMAQdx VIs
Compatibility VIs
For VIs that do not have a direct mapping, we are providing an NI-IMAQdx Compatibility for NI-IMAQ API to facilitate the migration.
These VIs are drop-in replacements for current NI-IMAQ VIs. Each compatibility VI retains the behavior of the NI-IMAQ VI but instead uses the NI-IMAQdx API. These VIs offer a quick way of transitioning from using the NI-IMAQ API to using the NI-IMAQdx API while keeping the VI behavior the same. They are also good reference examples on how to use the NI-IMAQdx API with a Camera Link device. Looking at the block diagram of the compatibility VIs illustrates how to implement NI-IMAQ features with the NI-IMAQdx API.
The name for each compatibility VI is of the form “NI-IMAQdx Compatibility - <NI-IMAQ VI name>.vi” and can be found in “C:\Program Files\National Instruments\LabVIEW XXXX\vi.lib\vision\driver\IMAQdxCompatibilityForIMAQ.llb”.
These VIs will not show up in the Functions palette in LabVIEW. Use them from the LLB directly, or export the LLB to a folder and drag and drop them in LabVIEW.
Below is the full list of compatibility VIs. The connector panes for the compatibility VIs are identical to the NI-IMAQ VI they replace, and, therefore, they should serve as a drop-in replacement. If an NI-IMAQ VI in this list has an input terminal that is not found in the corresponding compatibility VI (e.g. Step x, Step y, Channel, Region of Interest), this feature is not implemented in NI-IMAQdx. The detailed help for each of these compatibility VIs points to the NI-IMAQ documentation as the functionality is the same.
NI-IMAQ VI Name | Compatibility VI Name |
IMAQ Configure Trigger3.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Configure Trigger3.vi |
IMAQ Copy Acquired Buffer.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Copy Acquired Buffer.vi |
IMAQ Extract Buffer.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Extract Buffer.vi |
IMAQ Generate Pulse3.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Generate Pulse3.vi |
IMAQ Get Buffer.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Get Buffer.vi |
IMAQ Get Camera Attribute.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Get Camera Attribute.vi |
IMAQ Grab Acquire.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Grab Acquire.vi |
IMAQ Reset Encoder Position.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Reset Encoder Position.vi |
IMAQ Sequence.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Sequence.vi |
IMAQ Serial Write.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Serial Write.vi |
IMAQ Set Camera Attribute.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Set Camera Attribute.vi |
IMAQ Snap.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Snap.vi |
IMAQ Status.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Status.vi |
IMAQ Trigger Drive2.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Trigger Drive2.vi |
IMAQ Trigger Read2.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Trigger Read2.vi |
IMAQ Trigger Route2.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Trigger Route2.vi |
IMAQ Wait Signal2.vi | IMAQdx Compatibility – IMAQ Wait Signal2.vi |
Figure 2. Mapping of NI-IMAQ to Compatibility VIs
Attribute Translation
Migrating NI-IMAQ VIs to NI-IMAQdx VIs is usually a fairly simple process of replacing the NI-IMAQ VI with the corresponding NI-IMAQdx VI or compatibility VI. However, if the application is using LabVIEW property nodes, the porting from NI-IMAQ to NI-IMAQdx is more involved.
Figure 4 below gives a mapping of relevant NI-IMAQ attributes to the corresponding attributes in NI-IMAQdx. In the left column, you will find the NI-IMAQ attributes listed by their LabVIEW property node layout and their C attribute identifier, as found in niimaq.h. In the right column, the corresponding fully qualified NI-IMAQdx attribute name is shown followed by the LabVIEW property node location if the attribute has a direct mapping to the NI-IMAQdx property node.
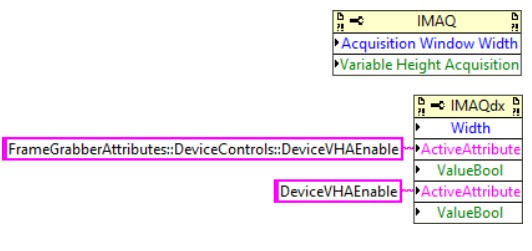
Figure 3 below shows an example of a property node with two NI-IMAQ attributes on top and a corresponding property node for these same attributes in NI-IMAQdx below. If a property node location is listed for an NI-IMAQdx attribute in the table below, then that attribute maybe be set in a manner like the “Width” attribute. However, if there is not a property node location listed in the table for the NI-IMAQdx attribute, then the “Active Attribute” must first be set to the name of the attribute that you wish to interact with followed by the “Value”. The “Active Attribute” can be specified by either the fully qualified name or the leaf name as shown for the “DeviceVHAEnable” attribute below. To ensure that all of the attribute sets and gets are being performed on the desired attribute, always put the “Active Attribute” and “Value” nodes for a given attribute in the same instance of a property node rather than setting the “Active Attribute” in one property node instance and performing the set or get to the “Value” in another property node instance.
Figure 3. NI-IMAQ Acquisition Window Width conversion to NI-IMAQdx Property Node
If the NI-IMAQ attribute that you are using is not shown in the table below, then it was either deemed deprecated or did not have a direct mapping to an NI-IMAQdx attribute. Consider if the attribute is necessary to your application or if you can accomplish the same goal by using other NI-IMAQdx attributes. If you find that you still need the information provided by the NI-IMAQ attribute, contact National Instruments for support.
NI-IMAQ Property Node / Attribute Constant | NI-IMAQdx Attribute Name / Property Node |
Acquisition Parameters:Acquisition Window:Height IMG_ATTR_ACQWINDOW_HEIGHT | FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::Height Acquisition Attributes:Height |
Acquisition Parameters:Acquisition Window:Left IMG_ATTR_ACQWINDOW_LEFT | FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::OffsetX Acquisition Attributes:Offset X |
Acquisition Parameters:Acquisition Window:Top IMG_ATTR_ACQWINDOW_TOP | FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::OffsetY Acquisition Attributes:Offset Y |
Acquisition Parameters:Acquisition Window:Width IMG_ATTR_ACQWINDOW_WIDTH | FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::Width Acquisition Attributes:Width |
Acquisition Parameters:External Trigger Line Filter IMG_ATTR_EXT_TRIG_LINE_FILTER | FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls::LineFilterTTLEnable |
Acquisition Parameters:Frame Timeout (ms) IMG_ATTR_FRAMEWAIT_MSEC | AcquisitionAttributes::Timeout Acquisition Attributes:Timeout |
Acquisition Parameters:Number of Post Trigger Buffers IMG_ATTR_NUM_POST_TRIGGER_BUFFERS | FrameGrabberAttributes::AcquisitionControls::BuffersAfterAcqEndTrigger |
Acquisition Parameters:RTSI Trigger Line Filter IMG_ATTR_RTSI_LINE_FILTER | FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls::LineFilterRTSIEnable |
Acquisition Parameters:Variable Height Acquisition IMG_ATTR_VHA_MODE | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls::DeviceVHAEnable |
Device Information:Interface Type IMG_ATTR_INTERFACE_TYPE | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls::DeviceInterfaceType |
Device Information:Linescan Camera IMG_ATTR_LINESCAN | CameraAttributes::DeviceControls::DeviceScanType |
Device Information:Number of External Trigger Lines IMG_ATTR_NUM_EXT_LINES | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls:: DeviceLinesTTL |
Device Information:Number of ISO In Trigger Lines IMG_ATTR_NUM_ISO_IN_LINES | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls::DeviceLinesIsoIn |
Device Information:Number of ISO Out Trigger Lines IMG_ATTR_NUM_ISO_OUT_LINES | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls:: DeviceLinesIsoOut |
Device Information:Number of RTSI Trigger Lines IMG_ATTR_NUM_RTSI_LINES | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls:: DeviceLinesRTSI |
Device Information:Serial Number IMG_ATTR_GETSERIAL | CameraInformation::SerialNumberLow Camera Information:Serial Number Low |
Encoder:Divide Factor IMG_ATTR_ENCODER_DIVIDE_FACTOR | FrameGrabberAttributes::EncoderControls::EncoderDivider |
Encoder:Phase A & B Filter IMG_ATTR_ENCODER_FILTER | FrameGrabberAttributes::EncoderControls::EncoderFilterEnable |
Encoder:Phase A Polarity IMG_ATTR_ENCODER_PHASE_A_POLARITY | FrameGrabberAttributes::EncoderControls::EncoderPolarityA |
Encoder:Phase B Polarity IMG_ATTR_ENCODER_PHASE_B_POLARITY | FrameGrabberAttributes::EncoderControls:: EncoderPolarityB |
Encoder:Position (U64) IMG_ATTR_ENCODER_POSITION | FrameGrabberAttributes::EncoderControls::EncoderValue |
Encoder:Use IO Board Input IMG_ATTR_ENCODER_USE_IO_BOARD_INPUT | FrameGrabberAttributes::EncoderControls::EncoderUseIOBoardInput |
Image Parameters:Bayer:Algorithm IMG_ATTR_BAYER_ALGORITHM | AcquisitionAttributes::Bayer::Algorithm |
Image Parameters:Bayer:Blue Gain IMG_ATTR_BAYER_BLUE_GAIN | AcquisitionAttributes::Bayer::GainB Acquisition Attributes:Bayer:Gain B |
Image Parameters:Bayer:Green Gain IMG_ATTR_BAYER_GREEN_GAIN | AcquisitionAttributes::Bayer::GainG Acquisition Attributes:Bayer:Gain G |
Image Parameters:Bayer:Onboard Decode Enable IMG_ATTR_BAYER_ONBOARD_DECODE_ENABLE | AcquisitionAttributes::Bayer::OnboardDecodeEnable |
Image Parameters:Bayer:Onboard Decode Force RGB32 IMG_ATTR_BAYER_ONBOARD_DECODE_FORCE_RGB32 | AcquisitionAttributes::Bayer::OnboardDecodeForceRGB32 |
Image Parameters:Bayer:Pattern IMG_ATTR_BAYER_PATTERN | AcquisitionAttributes::Bayer::Pattern Acquisition Attributes:Bayer:Pattern |
Image Parameters:Bayer:Red Gain IMG_ATTR_BAYER_RED_GAIN | AcquisitionAttributes::Bayer::GainR Acquisition Attributes:Bayer:Gain R |
Image Parameters:Binary Threshold High IMG_ATTR_BIN_THRESHOLD_HIGH | FrameGrabberAttributes::LUTControls::LUTBinaryThresholdHigh |
Image Parameters:Binary Threshold Low IMG_ATTR_BIN_THRESHOLD_LOW | FrameGrabberAttributes::LUTControls::LUTBinaryThresholdLow |
Image Parameters:Image Type IMG_ATTR_IMAGE_TYPE | Not needed. NI-IMAQdx will cast images to the correct type. You can query the image type using the Vision Development Module API. |
Image Parameters:Invert IMG_ATTR_INVERT | FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageFormatControls::ReverseY |
Image Parameters:Look-Up Table IMG_ATTR_LUT | FrameGrabberAttributes::LUTControls::LUT |
Status Information:Acquisition in Progress IMG_ATTR_ACQ_IN_PROGRESS | StatusInformation::AcqInProgress Status Information:Acquisition In Progress |
Status Information:Frame Count IMG_ATTR_FRAME_COUNT | StatusInformation::LastBufferCount Status Information:Last Buffer Count |
Status Information:Last Valid Frame IMG_ATTR_LAST_VALID_FRAME | StatusInformation::LastBufferNumber Status Information:Last Buffer Number |
Status Information:Lost Frames IMG_ATTR_LOST_FRAMES | StatusInformation::LostBufferCount Status Information:Lost Buffer Count |
Status Information:Power Over Camera Link IMG_ATTR_POCL_STATUS | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls::DevicePoCLStatus |
Status Information:Power Over Camera Link Base IMG_ATTR_POCL_STATUS_BASE | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls::DevicePoCLStatusBase |
Status Information:Power Over Camera Link Med/Full IMG_ATTR_POCL_STATUS_MED_FULL | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls::DevicePoCLStatusMediumFull |
Status Information:Temperature IMG_ATTR_TEMPERATURE | FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls::DeviceTemperature |
Figure 4. Mapping of NI-IMAQ to NI-IMAQdx Properties
Additional NI-IMAQdx Attributes
The full list of attributes can be seen in NI-MAX. First select your device in Devices and Interfaces tree in the left view. Then select the Camera Attributes tab in the right view. By default, only the “Camera Attributes” category is visible. This is where any attributes that have been defined in the NI-IMAQ camera file will be enumerated. To view the entire tree of available attributes, click “View Options” in the toolbar above the attribute tree, and select “All Attributes”.
Interact with the “Camera Attributes”, the same way that you would with other attributes. First set the “Active Attribute” in the LabVIEW property node to the name of the attribute, and then set the “Value”. Numeric attributes can be set as a double, and enumerated attributes can be set as a string.
The NI-IMAQdx API exposes the triggering and I/O functionality of the frame grabber using a GenICam-like attribute model rather than through a set of VIs as with the NI-IMAQ API. The compatibility VIs are implemented using these NI-IMAQdx attributes. The compatibility VIs can be used to provide a familiar experience when migrating an application from NI-IMAQ to NI-IMAQdx, or the NI-IMAQdx attributes may be used directly. Below is a list of the additional triggering and I/O attributes available that have not already been listed in the Attribute Translation section.
NI-IMAQdx Attribute Name |
FrameGrabberAttributes::AcquisitionControls::AcquisitionBurstFrameCount |
FrameGrabberAttributes::AcquisitionControls::TriggerSelector |
FrameGrabberAttributes::AcquisitionControls::TriggerMode |
FrameGrabberAttributes::AcquisitionControls::TriggerSource |
FrameGrabberAttributes::AcquisitionControls::TriggerActivation |
FrameGrabberAttributes::AcquisitionControls::TriggerDivider |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DeviceControls::PoCLEnable |
FrameGrabberAttributes:: DeviceControls::DeviceSerialActionCommandsEnable |
FrameGrabberAttributes:: DeviceControls::DeviceSerialPortBaudRate |
FrameGrabberAttributes:: DeviceControls:: DeviceSerialPortDataBits |
FrameGrabberAttributes:: DeviceControls:: DeviceSerialPortStopBits |
FrameGrabberAttributes:: DeviceControls:: DeviceSerialPortParityBit |
FrameGrabberAttributes:: DeviceControls:: DeviceSerialPortDTRPolarity |
FrameGrabberAttributes:: DeviceControls:: DeviceSerialPortRTSPolarity |
FrameGrabberAttributes:: DeviceControls:: DeviceSerialTerminationString |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls::LineSelector |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls:: LineMode |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls:: LineInverter |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls:: LineStatus |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls:: LineStatusAll |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls:: LineSource |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls::LineFormat |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls:: UserOutputSelector |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls:: UserOutputValue |
FrameGrabberAttributes::DigitalIOControls:: UserOutputValueAll |
FrameGrabberAttributes::EncoderControls::EncoderResetPosition |
FrameGrabberAttributes::ImageSizeControls::PayloadSize |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorSelector |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorMode |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorTriggerSource |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorTriggerActivation |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorTimerSource |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorDelay |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorDuration |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorDelayEncoderCounts |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorDurationEncoderCounts |
FrameGrabberAttributes::PulseGeneration::PulseGeneratorEnable |
Figure 5. New NI-IMAQdx Attributes
Error Code Translation
Camera Link support in NI-IMAQdx still makes use of the NI-IMAQ driver. Therefore, when using Camera Link devices, NI-IMAQdx VIs can emit NI-IMAQ error codes. If the NI-IMAQ error code is in the list below, it will automatically be converted into the corresponding NI-IMAQdx error code before being returned. If the NI-IMAQ error code is not in the list, it will be returned as-is without translation.
In addition, the system can send commands and data to other devices, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and operator interfaces, using industrial protocols such as Ethernet/IP, RS232/RS485, Modbus serial, and Modbus/TCP. Compact Vision Systems also have a dedicated Gigabit Ethernet port for network connectivity and two high-speed USB ports for external data storage. With enterprise connectivity, you can also monitor the inspection results, view images, or store data in databases for statistical process control.
NI-IMAQ | NI-IMAQdx | |||
Error Name | Error Code | Error Name | Error Code | |
IMG_ERR_SYSTEM_MEMORY_FULL | -1074397181 | IMAQdxErrorSystemMemoryFull | -1074360320 | |
IMG_ERR_DRIVER_FAULT | -1074396947 | IMAQdxErrorInternal | -1074360319 | |
IMG_ERR_BAD_POINTER | -1074397027 | IMAQdxErrorInvalidPointer | -1074360317 | |
IMG_ERR_BAD_INTERFACE_FILE | -1074397163 | IMAQdxErrorInvalidInterface | -1074360316 | |
IMG_ERR_ADDRESS_OUT_OF_RANGE | -1074396946 | IMAQdxErrorInvalidAddress | -1074360314 | |
IMG_ERR_BAD_DEVICE_TYPE | -1074397022 | IMAQdxErrorInvalidDeviceType | -1074360313 | |
IMG_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED | -1074397183 | IMAQdxErrorNotImplemented | -1074360312 | |
IMG_ERR_DEVICE_NOT_FOUND | -1074397029 | IMAQdxErrorCameraNotFound | -1074360311 | |
IMG_ERR_DEVICE_IN_USE | -1074396995 | IMAQdxErrorCameraInUse | -1074360310 | |
IMG_ERR_BOARD_NOT_INITIALIZED | -1074397046 | IMAQdxErrorCameraNotInitialized | -1074360309 | |
IMG_ERR_BOARD_CLOSED | -1074396961 | IMAQdxErrorCameraRemoved | -1074360308 | |
IMG_ERR_BOARD_RUNNING | -1074397151 | IMAQdxErrorCameraRunning | -1074360307 | |
IMG_ERR_BOARD_NOT_RUNNING | -1074397154 | IMAQdxErrorCameraNotRunning | -1074360306 | |
IMG_ERR_INVALID_ATTRIBUTE | -1074397098 | IMAQdxErrorAttributeNotSupported | -1074360305 | |
IMG_ERR_INVALID_BUFFER_ATTRIBUTE | -1074397025 | IMAQdxErrorAttributeNotSupported | -1074360305 | |
IMG_ERR_INVALID_CAMERA_ATTRIBUTE | -1074396962 | IMAQdxErrorAttributeNotSupported | -1074360305 | |
IMG_ERR_ATTRIBUTE_NOT_SETTABLE | -1074397116 | IMAQdxErrorAttributeNotSettable | -1074360304 | |
IMG_ERR_ATTRIBUTE_NOT_READABLE | -1074397101 | IMAQdxErrorAttributeNotReadable | -1074360303 | |
IMG_ERR_BUFFER_NOT_AVAILABLE | -1074397014 | IMAQdxErrorBufferNotAvailable | -1074360301 | |
IMG_ERR_NO_BUFFERS_CONFIGURED | -1074397158 | IMAQdxErrorBufferListEmpty | -1074360300 | |
IMG_ERR_BUFFER_LIST_ALREADY_LOCKED | -1074397023 | IMAQdxErrorBufferListLocked | -1074360299 | |
IMG_ERR_BUFFER_LIST_NOT_LOCKED | -1074397165 | IMAQdxErrorBufferListNotLocked | -1074360298 | |
IMG_ERR_TIMEOUT | -1074397150 | IMAQdxErrorTimeout | -1074360293 | |
IMG_ERR_CANNOT_WRITE_FILE | -1074396912 | IMAQdxErrorFileAccess | -1074360290 | |
IMG_ERR_CANNOT_READ_FILE | -1074396911 | IMAQdxErrorFileAccess | -1074360290 | |
IMG_ERR_BAD_CAMERA_FILE | -1074397160 | IMAQdxErrorInvalidCameraFile | -1074360288 | |
IMG_ERR_INSTALLATION_CORRUPT | -1074396952 | IMAQdxErrorDLLNotFound | -1074360284 | |
IMG_ERR_VIDEO_LOCK | -1074397153 | IMAQdxErrorCameraUnreachable | -1074360276 | |
IMG_ERR_SERIAL_READ_TIMEOUT | -1074397037 | IMAQdxErrorTimeout | -1074360293 | |
IMG_ERR_SERIAL_WRITE_TIMEOUT | -1074397036 | IMAQdxErrorTimeout | -1074360293 | |
Figure 6. NI-IMAQ to NI-IMAQdx error code mapping
NI-IMAQ functionality not supported in NI-IMAQdx
Some NI-IMAQ VIs do not have compatibility or direct replacements in the NI-IMAQdx API.
The following VIs are not supported in NI-IMAQdx.
NI-IMAQ VI Name | Comments | |
IMAQ Occurrence Config2.vi | Occurrences are not supported through the NI-IMAQdx driver. Use asynchronous events instead. See example VI “C:\Program Files (x86)\National Instruments\LabVIEW 2018\examples\Vision Acquisition\NI-IMAQdx\Low Level\Low-Level Grab Async.vi”. | |
IMAQ Configure List.vi | NI-IMAQdx does not require that you configure a buffer list. You can either remove this VI completely or replace with NI-IMAQdx Ring Acquisition VIs. | |
IMAQ Configure Buffer.vi | NI-IMAQdx does not require that you configure each individual buffer used in the acquisition. NI-IMAQdx does not support the “skip count” feature. You can either remove this VI completely or replace with NI-IMAQdx Ring Acquisition VIs. | |
IMAQ Fit ROI.vi | This behavior is not directly supported in NI-IMAQdx. Set the “Width”, “Height”, “OffsetX, and “OffsetY” attributes to emulate the behavior. | |
IMAQ Set User LUT.vi | This feature is not supported by any Camera Link boards that can be used in NI-IMAQdx. | |
Figure 7. Unsupported NI-IMAQ functions in NI-IMAQdx
Camera Files for Camera Link cameras using NI-IMAQdx
Camera Link devices in NI-IMAQdx make use of both NI-IMAQdx and NI-IMAQ camera files.
Similar to using a Camera Link camera in NI-IMAQ, the camera attributes are stored in the NI-IMAQ .icd file located in the “Documents/National Instruments/NI-IMAQ/Data” folder. There are also some frame grabber attributes that are stored in this camera file. When converting an application from the NI-IMAQ API to the NI-IMAQdx API, no changes to this file are needed. Note that NI-IMAQ camera files are only used with Camera Link devices; using NI-IMAQdx with cameras on other buses will not use the NI-IMAQ camera files at all.
In addition to the NI-IMAQ .icd and .iid files, when using the NI-IMAQdx API, each Camera Link camera will have associated NI-IMAQdx .iid and .icd files located in the “Documents/National Instruments/NI-IMAQdx/Data” folder. The NI-IMAQdx .icd file stores additional frame grabber attributes that are not stored in the NI-IMAQ camera file (e.g. triggering and I/O settings). To deploy a configuration to another system, it is necessary to copy both the NI-IMAQ and NI-IMAQdx .iid and .icd files to the new system.