Find the Right Analog Signal Generator
Overview
Contents
Analog Output
Analog output instruments provide static or dynamic multichannel analog output signals. They enable you to create applications such as stimulus-response, power supply control, deterministic control, and sensor/signal simulation. Analog Output Devices offer various output resolutions, channel counts, and other onboard features, so you can replace several kinds of instruments in your system, including stand-alone proportional integral derivative (PID) controllers, low-speed arbitrary waveform generators, and function generators. Basic, DAC-based analog output devices should generally only be used for low-speed waveform and static generation applications.
Dynamic Signal Sources
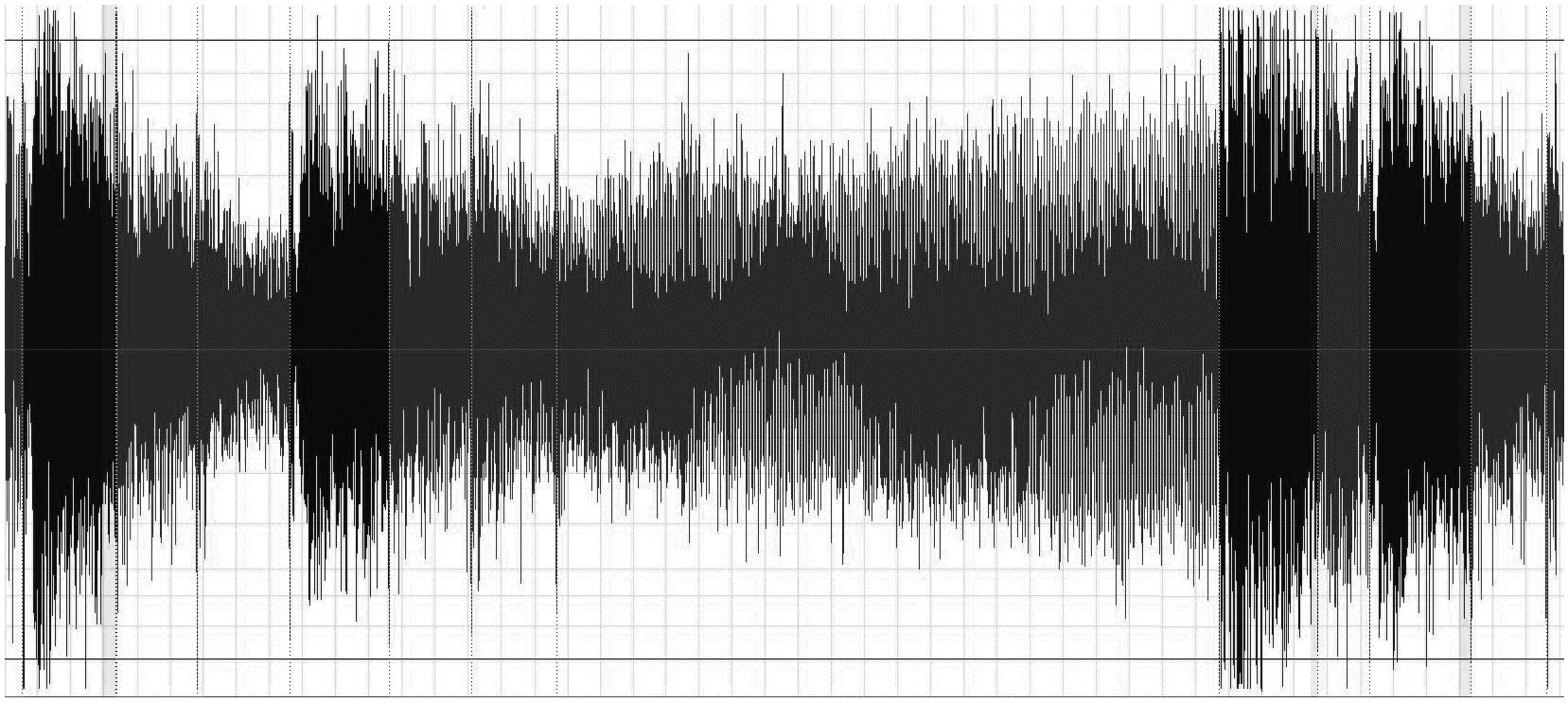
Dynamic signal instruments are designed specifically for applications like audio test and measurement, noise and vibration diagnostics, machine condition monitoring, automotive test, noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) analysis, laboratory research, and any other applications that require very large dynamic range and excellent signal flatness. They provide software-configurable AC/DC coupling, antialiasing filters, and IEPE conditioning to ensure precision measurements with microphones, accelerometers, and other transducers with large dynamic ranges.
Learn more about dynamic signal generators
Figure 1: Dynamic signal generators are ideal for highly dynamic signals that require accuracy and flatness like sound waves.
Waveform Generators
Waveform Generators produce large, complex analog waveforms in a sequential manner or using real-time streaming. These instruments are ideal for applications in scientific research and testing of consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace/defense.
Learn more about waveform generators
Function Generators
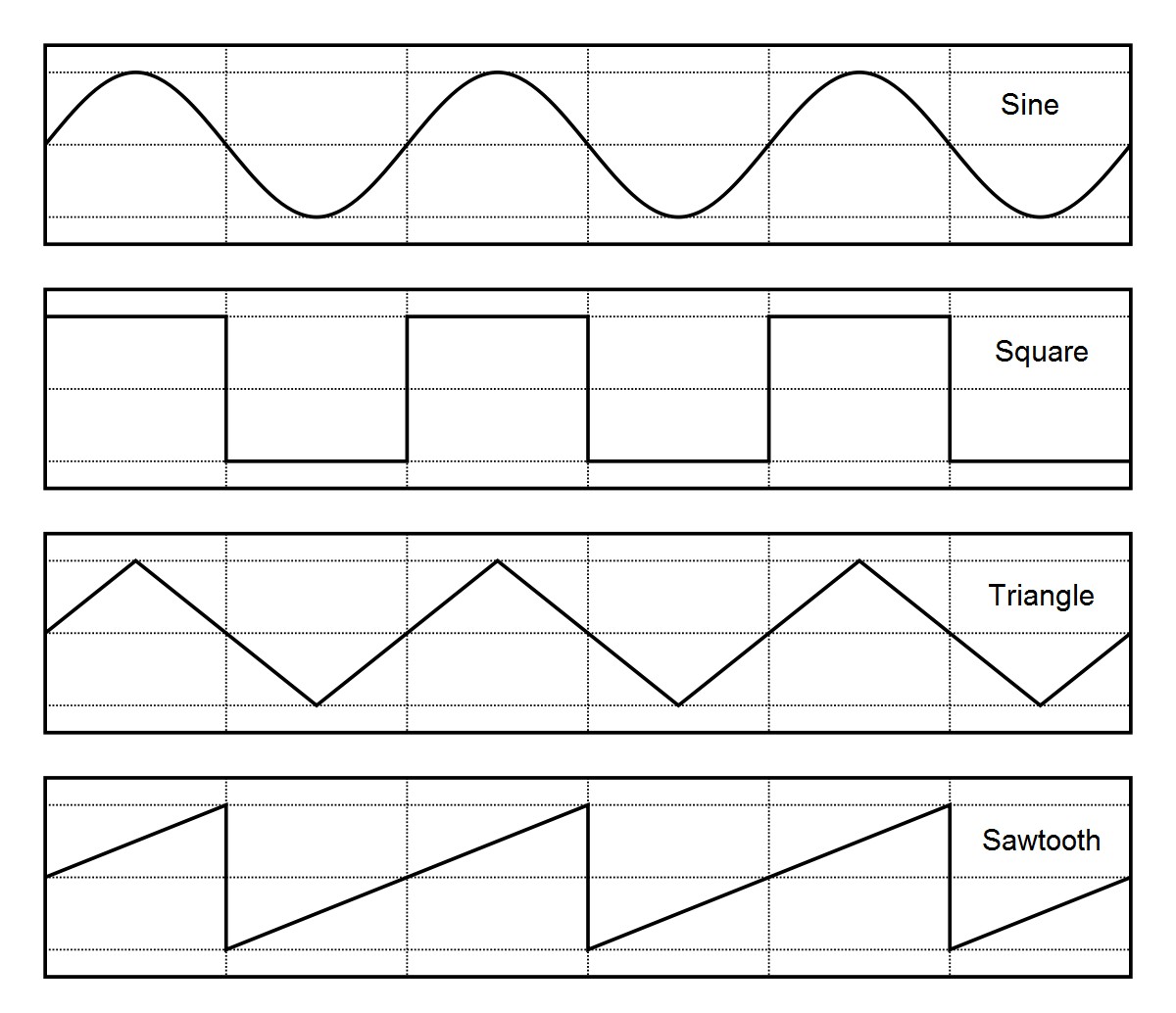
Function generators can produce precise waveforms including sine, square, triangle, and ramp with very high signal purity and accuracy. These instruments are ideal for validation, verification, and production test of semiconductor devices, consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace/defense that only require repetitive signals to ensure proper functionality.
Learn more about function generators
Figure 2: Function generators can accurately generate a number of standard, repetitive waveforms.
Arbitrary Waveform Generators
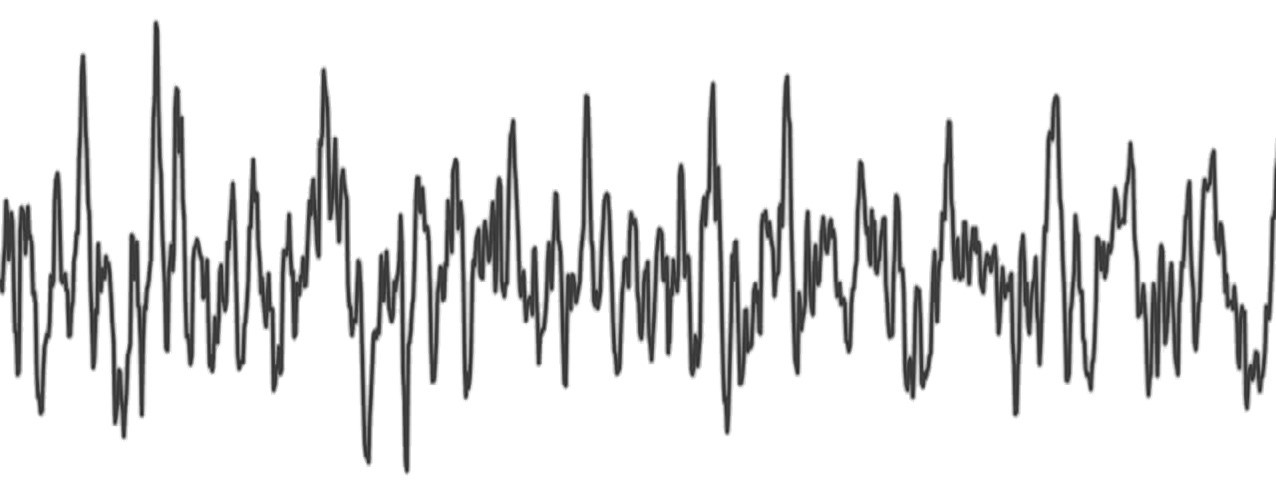
Arbitrary waveform generators can produce precise waveforms including sine, square, triangle, and ramp as well as arbitrary, user-defined waveforms. When used in modular instrumentation platforms like PXI, arbitrary waveform generators often allow user to create sequences of waveforms or enable streaming continuously from a host or peer-to-peer instrument. These instruments are ideal for tightly synchronized, mixed-signal test systems in scientific research or test of semiconductor devices, consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace/defense that require multiple types of input signals and flexible generation capabilities.
Learn more about arbitrary waveform generators
Figure 3: Arbitrary waveform generators can produce signals with user-defined values. Some arbitrary waveform generators have a lot of memory for very long waveforms, have the ability to generate different pieces of waveform according to a script, or can stream waveform data from a host for a continuously variable signal over time.
Pulse Generators
Pulse generators are used to create rectangular pulses with controllable duty cycle, rise and fall time, and amplitude with very low edge and trigger jitter. Pulse generators are used for verification, validation, and production functional test in the aerospace/defense, semiconductor, and automotive industries.
RF Signal Generators
RF signal generators produce different types of signals—ranging from pulsed to modulated to continuous wave. You can use these instruments for RFIC testing, radar and electronic warfare, automated test, and other applications.
Vector Signal Generators
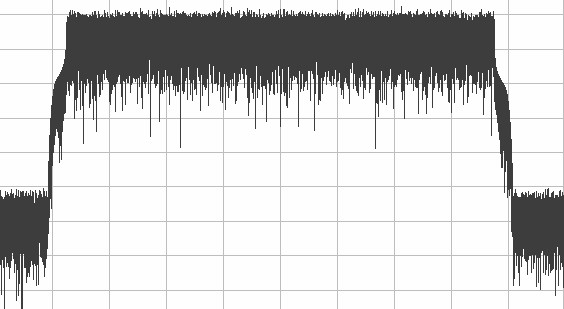
Vector signal generators offer custom and standard modulation, as well as the ability to generate communications standards formats such as GPS, WCDMA, DVB-H, and more. They support quadrature digital upconversion, which reduces waveform download and signal generation time. Vector signal generators in module instrumentation form factors like PXI often offer stream-to-disk and scripting capabilities. The vector signal generators are ideal for use in scientific research, communications, consumer electronics, aerospace/defense, and semiconductor test applications as well as for areas such as software-defined radio, radio-frequency identification (RFID), and wireless sensor networks.
Figure 4: Vector signal generators can be used to output data over a number of RF communication standards like those used in cellular or Wi-Fi as well as arbitrary signals for communications and other applications.
RF Analog Signal Generators
RF analog signal generators support frequency ranges from 250 kHz to 20 GHz. RF analog signal generators in modular instrumentation platforms like PXI can be combined with other instruments to design automated test systems for radar, RF integrated circuits (RFICs), and automotive test applications.
Learn more about RF analog signal generators
Figure 5: RF analog signal generators can be used to output a number of standard or arbitrary signals at baseband or that can be mixed with high frequency signal conditioning instrumentation to be centered around carrier frequencies for communications and other applications.