Transitioning From Compact FieldPoint to CompactRIO
Overview
Contents
- General Comparison of Compact FieldPoint and CompactRIO
- I/O Module Transition Guide
- Ethernet Interface Migration Options
- Application Programming
- Programming CompactRIO With LabVIEW FPGA
Both Compact FieldPoint and CompactRIO offer rugged specifications and industrial I/O that are programmed in the same LabVIEW graphical development environment. In general, CompactRIO systems offer higher performance and more flexibility than Compact FieldPoint systems at similar price points.
General Comparison of Compact FieldPoint and CompactRIO
The following comparison table shows some of the primary features and capabilities of the two product lines and the maximum specifications that are available in each:
| Feature | Compact FieldPoint | CompactRIO |
|---|---|---|
| Processor Speed | 400 MHz | 1.91 GHz |
| Memory (RAM) | 256 MB | 2 GB |
| Storage | 256 MB | 16 GB |
| Analog Input Sampling Rate | 360 Hz | 1 MHz |
| Analog Input Resolution | 16 bits | 24 bits |
| Analog Output Update Rate | 200 Hz | 100 kHz |
| Analog Output Resolution | 12 bits | 16 bits |
| Analog Channels/Slot | 16 | 32 |
| Digital I/O Rates | 1 kHz | 40 MHz |
| Control Loop Speed | 10 kHz | 1 MHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40 °C to 70 °C | -40 °C to 70 °C |
| Shock | 50 G | 50 G |
| Vibration | 5 G | 5 G |
Compare CompactRIO controller options.
Browse pricing and specifications for CompactRIO controllers.
I/O Module Transition Guide
CompactRIO input and output (I/O) modules are called C Series modules. NI offers more than 100 C Series modules, so you can generally find a direct replacement for all Compact FieldPoint I/O modules.
Use the following tables as guides to migrate Compact FieldPoint I/O modules to CompactRIO C Series modules.
Analog I/O Modules
| Measurement Type | Compact FieldPoint Module | Similar CompactRIO Module | Notable Specification Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Input | cFP-AI-111 16 Ch, ±20 mA Input | NI 9208 16 Ch, ±21.5 mA Input | - |
| RTD | cFP-RTD-122 2- and 3-Wire, 8 Ch, 0–4000 Ω Input | NI 9226 2-, 3-, and 4-Wire; 8 Ch; 0–4000 Ω Input | - |
| cFP-RTD-124 2- and 4-Wire, 8 Ch, 0–400 Ω Input | NI 9216 2-, 3-, and 4-Wire; 8 Ch; 0–400 Ω Input | - | |
| Strain | cFP-SG-140 8 Ch, Full/Half Bridge | NI 9237 4 Ch, Full/Half/Quarter Bridge | The cFP-SG-140 has eight channels with a maximum input range of ±60 mV/V, whereas the NI 9237 has four channels with a maximum input range of ±25 mV/V. |
| Thermocouple | cFP-TC-120 8 Ch Thermocouple | - | |
| cFP-TC-125 8 Ch, Ch-Ch ISO Thermocouple | NI 9212 8 Ch, Ch-Ch ISO Thermocouple | - | |
| Voltage Input | cFP-AI-102 8 Ch, ±120 V Input | NI 9221 8-Ch +/-60 V Input | - |
| cFP-AI-112 16 Ch, ±10 V Input | NI 9205 32 Ch, ±10 V Input | - | |
| cFP-AI-118 8 Ch, ±15 V Ch-Ch ISO Input | NI 9239 4 Ch, ±10 V Ch-Ch ISO Input | The cFP-AI-118 has a maximum input range of ±15 V with 750 V of continuous channel-to-channel isolation, whereas the NI 9239 has a maximum input range of ±10 V with 250 V of continuous channel-to-channel isolation. | |
| Voltage/Current Combo Input | cFP-AI-100 8 Ch, ±30 V, ±20 mA Input | NI 9207 8 Ch, ±10 V, 8 Ch, ±20 mA Input | - |
| cFP-AI-110 8 Ch, ±10 V, ±20 mA Input | NI 9207 8 Ch, ±10 V, 8 Ch, ±20 mA Input | - | |
| Voltage/Current Input, Current Output | cFP-AIO-600 4 Ch Input, 4 Ch 0–20 mA Output | NI 9207 8 Ch, ±10 V, 8 Ch, ±20 mA Input NI 9221 8 Ch, ±60 V Input NI 9265 4 Ch, 0–20 mA Output | There is no direct replacement for the cFP-AIO-600, so multiple CompactRIO C Series modules should be considered.
|
| Voltage/Current Input, Voltage Output | cFP-AIO-610 4 Ch Input; 4 Ch, ±10 V Output | NI 9207 8 Ch, ±10 V, 8 Ch, ±20 mA Input NI 9221 8 Ch, ±60 V Input NI 9263 4 Ch, ±10 V Output | There is no direct replacement for the cFP-AIO-610, so multiple CompactRIO C Series modules should be considered.
|
| Current Output | cFP-AO-200 8 Ch, 0–20 mA Output | NI 9266 8 ch, 0–20 mA Output | - |
| Voltage Output | cFP-AO-210 8 Ch, 0–10 V Output | NI 9263 4-Ch +/-10 V Output NI 9264 16 Ch, ±10 V Output | - |
Digital I/O Modules
| Measurement Type | Compact FieldPoint Module | Similar CompactRIO Module | Notable Specification Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sinking Input | cFP-DI-300 8 Ch, 0–30 V Digital Input | NI 9421 8 Ch, 0–30 V Digital Input | - |
| cFP-DI-301 16 Ch, 0–30 V Digital Input | NI 9421 8 Ch, 0–30 V Digital Input NI 9425 32 Ch, 0–30 V Digital Input | - | |
| cFP-DI-304 32 Ch, 0–30 V Digital Input | NI 9425 32 Ch, 0–30 V Digital Input | - | |
| Sinking/Sourcing Input | cFP-DI-330 8 Ch, 0–250 V Digital Input | NI 9437 8 Ch, 24–250 VDC Digital Input | The cFP-DI-330 is a sinking/sourcing digital input module with a 0-250 VDC/VAC maximum input range, whereas the NI 9437 is a sinking digital input module with a 24-250 VDC maximum input range. |
Sinking/Sourcing Input, Sourcing Output | cFP-DIO-550 8 Ch Input, 8 Ch Output | NI 9375 16 Ch Input, 16 Ch Output | The cFP-DIO-550 has eight channels of sinking/sourcing digital input, whereas the NI 9375 has sixteen channels of sinking digital input. |
| Relay | cFP-RLY-421 8 Ch, 0–250 V SPST 10 Hz Relay | NI 9482 4 Ch, 0–250 V SPST 1 Hz Relay | The cFP-RLY-421 has eight relay channels with a maximum switching frequency of 10 Hz, whereas the NI 9482 has four relay channels with a maximum switching frequency of 1 Hz. |
| cFP-RLY-423 4 Ch, 0–250 V SPDT 10 Hz Relay | NI 9482 4 Ch, 0–250 V SPST 1 Hz Relay | There is no SPDT replacement in CompactRIO. The NI 9482 is a 4-channel SPST relay module with a maximum switching frequency of 1 Hz. | |
| cFP-RLY-425 8 Ch, 0–250 V SPST 0.5 Hz Relay | NI 9482 4 Ch, 0–250 V SPST 1 Hz Relay | The cFP-RLY-425 has eight relay channels with a maximum switching current of 3 A at 250 VAC and 5 A at 125 VAC. The NI 9482 has four relay channels with a maximum switching current of 1.5 A at 250 VAC. | |
| Sinking Output | cFP-DO-403 16 Ch, 5–30 V Digital Output | NI 9477 32 Ch, 5–60 V Digital Output | - |
| Sourcing Output | cFP-DO-400 8 Ch, 5–30 V Digital Output | NI 9472 8 Ch, 6–30 V Digital Output | - |
| cFP-DO-401 16 Ch, 5-30 V Digital Output | NI 9472 8 Ch, 6–30 V Digital Output NI 9476 32 Ch, 6–36 V Digital Output | - | |
| cFP-DO-410 8 Ch, 5–30 V TTL Digital Output | NI 9474 8 Ch, 5–30 V Digital Output | - | |
| Pulse Width Modulation | cFP-PWM-520 8 Ch, 5–30 V Digital Output | NI 9474 8 Ch, 5–30 V Digital Output¹ | - |
| Quadrature Encoder | cFP-QUAD-510 4 Ch ,1 MHz Input | NI 9411 6 Ch, 2 MHz Input¹ | - |
| Sinking Counter | cFP-CTR-500 8 Ch, 50 kHz Sink Counter | NI 9361 8 Ch, 1 MHz Sink Counter | - |
| Sourcing Counter | cFP-CTR-502 8 Ch, 50 kHz Source Counter | NI 9422 8 Ch, 4 kHz Sink/Source Digital Input¹ | The cFP-CTR-502 has a maximum clock rate of 50 kHz, whereas the NI 9422 has a maximum clock rate of 4 kHz. |
| Sinking Pulse Generation | cFP-PG-522 8 Ch, 5–30 V Sink Digital Output | NI 9474 8 Ch, 5–30 V Source Digital Output¹ | The cFP-PG-522 is a sinking digital output module with a maximum current drive of 16 A, whereas the NI 9474 is a sourcing digital output module with a maximum current drive of 8 A. |
¹Some CompactRIO modules have specialty digital function support in Scan Mode. See all specialty digital supported modules.
Ethernet Interface Migration Options
CompactRIO also provides options for expansion I/O over standard Ethernet similar to the cFP-1804 and cFP-1808.
The recommended migration options for those systems are:
| Compact FieldPoint Ethernet Interface | Similar CompactRIO Ethernet Expansion |
|---|---|
| cFP-1804 4-Slot Ethernet Interface | NI 9147 4-Slot Ethernet RIO Expansion Chassis |
| cFP-1808 8-Slot Ethernet Interface | NI 9149 8-Slot Ethernet RIO Expansion Chassis |
Application Programming
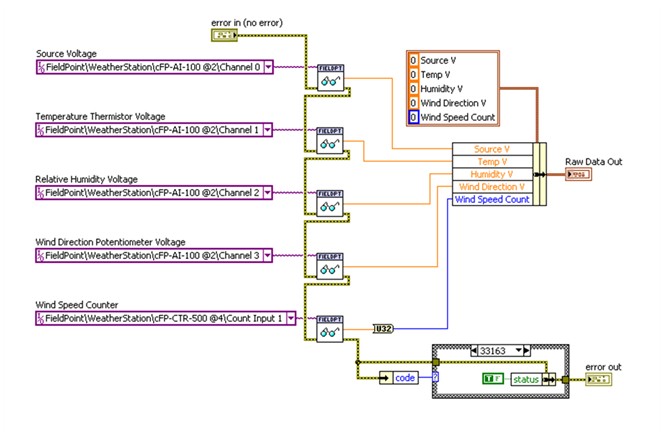
Both Compact FieldPoint and CompactRIO are programmed using LabVIEW to offer a similar programming experience. Figure 1 shows the block diagram of an example Compact FieldPoint application. Five channels are being read using the FP Read.vi functions.
Figure 1. Compact FieldPoint Programming Example Using FP Read.vi Function Calls
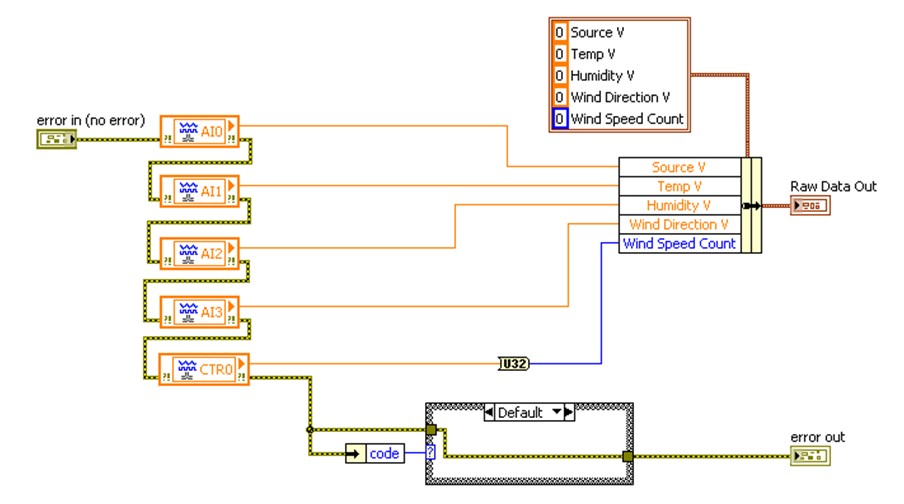
Instead of using FP Read.vi functions, a corresponding CompactRIO application would take measurements using I/O variables that you drag and drop from the LabVIEW Project Explorer. Figure 2 shows the same code from Figure 1 but with the FP Read.vi functions replaced with CompactRIO I/O variables.
Figure 2. CompactRIO I/O values are read using I/O variables instead of the previously used FieldPoint Read functions.
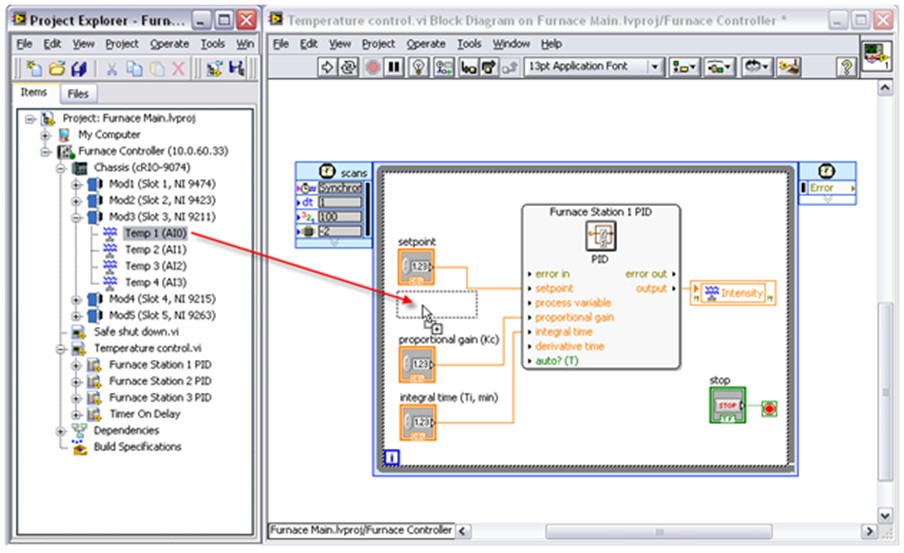
Each C Series I/O module is configured using the LabVIEW Project Explorer, and I/O variables appear as resources for use in the LabVIEW application. Figure 3 shows an example of an I/O variable being added to the block diagram for a control application by dragging and dropping it over.
Figure 3. CompactRIO I/O values are read by dragging and dropping I/O variables from the LabVIEW Project Explorer onto the block diagram.
I/O variables in the LabVIEW project take advantage of a special programming mode for CompactRIO called the Scan Interface mode, where I/O is continuously sampled at a fixed scan rate in hardware. The LabVIEW program can then read the current input value or set a new output value using the I/O variables in software.
Programming CompactRIO With LabVIEW FPGA
If you have the LabVIEW FPGA Module installed on your development computer, you can take advantage of the second programming mode for CompactRIO called FPGA mode.
FPGAs are reconfigurable chips that are included in every CompactRIO system. They provide high-speed control, custom triggering, and signal processing options for I/O.
Learn more about LabVIEW FPGA.
Watch short videos of how LabVIEW FPGA programming works with CompactRIO.